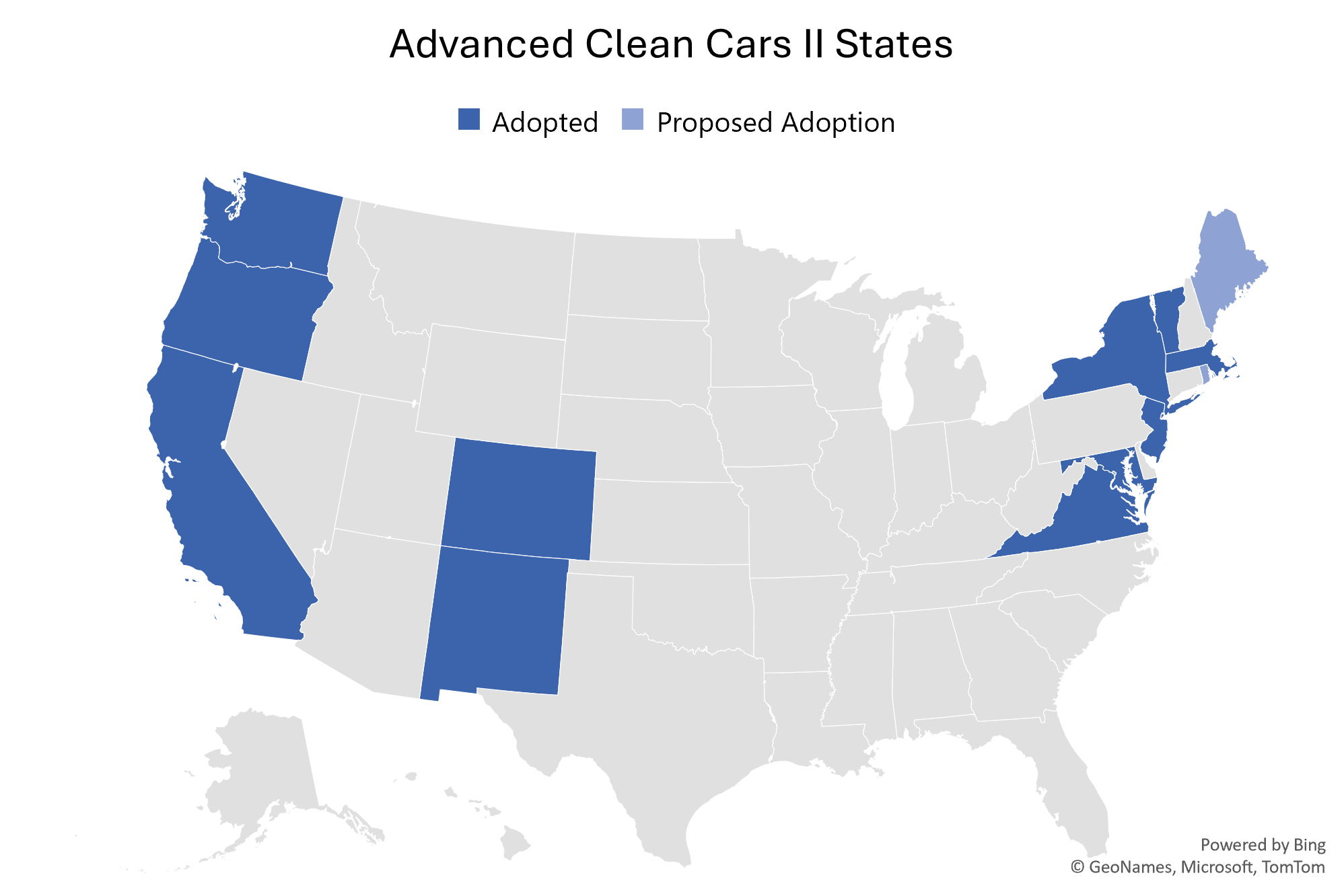
Last week, Delaware became the latest state to take regulatory action to accelerate electric vehicle adoption (EV) by adopting California’s Advanced Clean Cars II (ACC II) regulation.
Approved by the state last Wednesday, Delaware’s regulation will require automakers to deliver an increasing percentage of zero-emission vehicles, starting with 43 percent in model year 2027. However, unlike California’s standard, Delaware’s regulation will stop short of 100 percent ZEVs, instead maxing out at 82 percent in 2032. Delaware’s decision comes after New Mexico and New Jersey formally adopting the regulation earlier last month. Like Delaware, New Mexico only adopts California’s sales percentages through 2032, while New Jersey will require 100 percent ZEV sales beginning in 2035.
The three states joined a growing cohort of states taking steps to address air pollution from motor vehicles through the clean cars regulation. Since our last digest, the number of states pursuing the regulation has proliferated, growing to twelve states who have formally adopted the regulation plus three more who are still in the rulemaking process. While most states’ rulemakings have been successful, just last week Connecticut Governor Ned Lamont withdrew the state’s proposed regulation, citing a lack of support on a key legislative committee. State lawmakers plan to continue to work towards a compromise. Rulemakings are ongoing in Maine, Rhode Island, and the District of Columbia.
To recap, the California Air Resources Board (CARB) unanimously voted to approve ACC II on August 25th, 2022, which requires automakers to increase the proportion of zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) sales year by year. As laid out by California, the standard sets the annual percentage of new ZEV sales at 35 percent for model year 2026 which increases to 100 percent by model year 2035. However, for states that adopt ACC II in 2023, the regulation takes effect for vehicles beginning in model year 2027.
A total of 12 states have now adopted the regulation, and three states are in the process of adopting the regulation. A list of these states can be found below.
Adopted:
California: Adopted by CARB on August 25th, 2022
Oregon: Adopted by Oregon’s Department of Environmental Quality on December 19th, 2022
Washington: Adopted by the Washington Department of Ecology on December 19th, 2022
New York: Adopted by the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation via emergency rulemaking on December 29th, 2022
Massachusetts: Formally adopted by the state on March 30th, 2023
Vermont: Adopted both ACC II and the Advanced Clean Trucks (ACT) regulation in one rulemaking package by the Legislative Committee on Administrative Rules for Vermont on December 16th, 2022
Virginia: Virginia adopted the rule via a trigger law in 2022, which was established by a previous administration. However, current Governor Youngkin has voiced opposition to the law and has announced intention to reverse the law
Colorado: On October 20th, 2023, the Colorado Air Quality Control Commission adopted the Colorado Clean Cars Standard
Maryland: On September 18th,2023, Maryland finalized its rulemaking and adopted ACC II
Delaware: Adopted by the Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control on November 29th, 2023
New Mexico: Adopted ACC II and ACT in one rulemaking by the New Mexico Environmental Improvement Board on November 16th, 2023
New Jersey: On November 21st, Governor Phil Murphy and the Department of Environmental Protection announced the filing of the ACC II rule for adoption on December 18th
Proposed:
Rhode Island: On May 10th, 2023, Governor Dan McKee announced plans to adopt ACC II and ACT
District of Columbia (D.C.): On December 9th, 2022, the D.C. Department of Energy & Environment proposed the adoption of ACC II
Maine: On July 26th, 2023, Maine initiated its public comment process and is considering adoption of the rule